Celebrating Plants and People
-

Best Hope Against Disease Of Coffee Plants May Be A Small Snail
A new discovery raises an intriguing possibility for controlling coffee’s costliest pest, and it comes packed inside a small shell. .. Asian tramp snails, Bradybaena similaris, can consume large amounts of coffee rust before the disease can damage the plant. Leave one snail on a rust-covered leaf, and it can hoover up 30 percent of…
-

Why The Soil Microbiome No Longer Feeds Our Crops
“When plants are selected for a small handful of traits like making a bigger seed or faster growth, you can lose a lot of important traits relating to microbes along the way.” This evolutionary loss has turned into a loss for the environment as well. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Can This South African Shrub Solve Climate Change?
In an age of climate doom, it is understandable that people turn to simple-sounding solutions, (Click on title for full story.)
-

Is Gardening The Secret To A Long Life?
Many of the world’s centenarians share one common hobby: gardening. Could you extend your life and drop your stress by taking up the pursuit, too? (Click on title for full story.)
-

The Mother Of All Life On Earth… This Alga
Scientists have discovered the fossils of what may be the oldest green algae ever known. The newfound seaweed — called Proterocladus antiquus — lived about a billion years ago. And even though it was tiny, about 0.07 inches (2 millimeters) in length, the algae had a big role: It could produce oxygen through photosynthesis. (Click…
-

Plant-Eating Fish Holds Promise For Feeding A Hungry World
With climate change making the raising of livestock less sustainable, the discovery holds promise for developing new sources of protein for human consumption. In particular, it could be important for aquaculture, which is a possible alternative but is contending with the issue of what to feed the fish being raised. “Using plant-based food ingredients reduces…
-

Ancient Lava Flows Reveal Future Of Forests Without Large Fruit-Eating Animals
The researchers found that before permanent human settlements, forests were dominated by large fleshy-fruited plant species, usually big trees. During and after human settlement in the 17th Century, when fruit eating animals (frugivores) like giant tortoises and flying foxes went extinct on the island, these plants were found to be far less present and by…
-
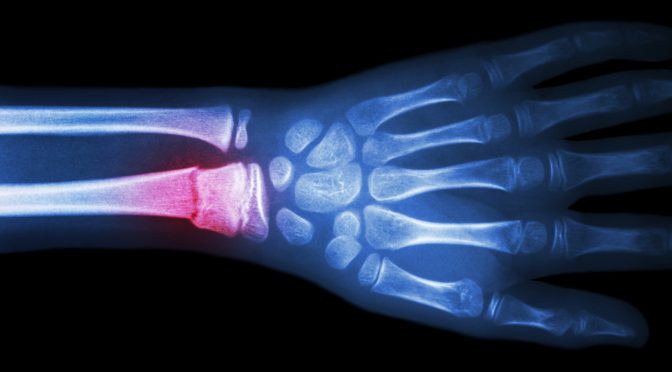
Lettuce Induced To Produce Bone-Healing Protein: A Game Changer For Diabetics And Others
In both mouse and human cells, the researchers showed that the plant-derived drug caused a variety of cell types, including oral-tissue cells and osteoblasts, or bone-building cells, to grow and differentiate, or divide to form a variety of different cell types. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Stealthy Possum Pollinates Flower And Confounds Scientists
In Brazil there is a plant so strange that researchers predicted – and 27 years later, proved – that opossums are key to its pollination. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Ancient Cereal Grains Prove Silk Road Trade Even Older Than Thought
These new discoveries seem to suggest that mixed small-scale human populations made major contributions to world history through migration and cultural and technological exchange. “This study not only presents the earliest dates for domesticated grains in far North Asia,it represents the earliest beginning of a trans-Eurasian exchange that would eventually develop into the great Silk…
