Celebrating Plants and People
-

American Bison Responsible for Producing Crops To Feed Indigenous Populations
“We don’t think of the plants they were eating as prairie plants,” she said. “However, this research suggests that they actually are prairie plants — but they only occur on prairies if there are bison. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Chinese Herbal Remedy Evolves To Hide From Greedy Humans
Here, we show that the leaf coloration of a herb used in traditional Chinese medicine (Fritillaria delavayi) varies among populations, with leaves matching their local backgrounds most closely. The degree of background matching correlates with estimates of harvest pressure, with plants being more cryptic in heavily collected populations. In a human search experiment, the time…
-
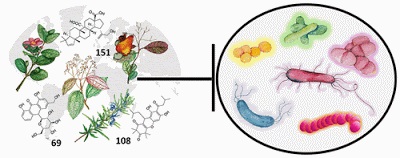
Natural Plant Products With Antibacterial Activity: A First And Much Needed Comprehensive Review Published
“We wanted to provide a systematic overview that brings promising drug candidates to the forefront, opening up new chemical space for discovery. Our review can serve as a starting point for chemists to consider whether they could possibly optimize any of these compounds to become scaffolds for antibiotics treatments.” (Click on title for full story.)
-

Can Leaf-Cutter Ants Teach Us To Farm Better?
“Ants have managed to retain a farming lifestyle across 60 million years of climate change, and Leafcutter ants appear able to grow a single cultivar species across diverse habitats, from grasslands to tropical rainforest” (Click on title for full story.)
-
When That Asteroid Destroyed The Dinosaurs It Pushed Algae To Become Carnivorous Hunters
Our fossil evidence allows us to identify an innovative ecological strategy in the post-extinction plankton communities, and our model outputs provide a theoretical explanation for this unique natural experiment in ocean ecosystem reconstruction. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Those Famous White Naturalists Who Made History Would Have Failed If Not For Their Enslaved Or Indigenous Assistants And Collaborators
Sloane, Darwin and Wallace are often credited with single-handedly changing the course of science as we know it, but their discoveries would not have been possible without the help of others. This help often came in the form of Indigenous people, enslaved Africans, Black healers, and others whose names and contributions have been lost to…
-

Even On Mars Healthy Plants Start With Healthy Soil
There are multiple ways you can look at it, but one option might be to use what’s already there as a potting medium, and figure out if that’s a viable way to do it or if you have to bring all the plant materials with you,” Fackrell said. “The question of whether we can use…
-
The Rare Tree That May Make Or Break COVID19 Vaccines’ Success
The bark is transformed into a brown, bitter, bubbly fluid. This precious goo does many things well, and it happens to be the raw material for one of the world’s most coveted vaccine adjuvants: QS-21. Adjuvants are compounds that boost the body’s immune reaction to a vaccine. Owing to their potential risks to human health,…
-

Urban Trees, Whether Native Or Introduced Species, Provide The Same Ecological And Social Services
“Should we promote native trees and ban – or at least put limits on – introduced species? Of all the species introduced into urban areas, only 5% are potentially problematic, such as the Tree of Heaven (Ailanthus altissima) located in the old town of Geneva. But what should we do with the remaining 95% of…
-
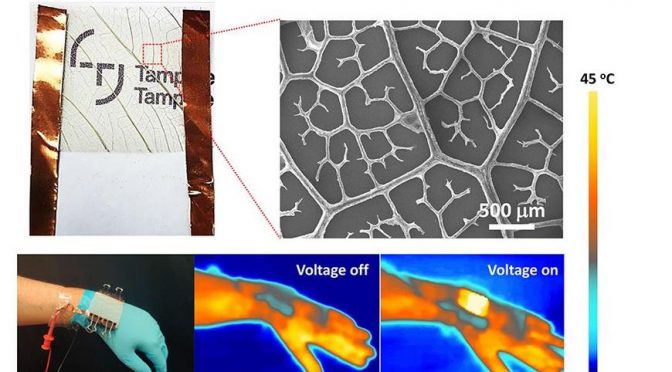
Turning To The Leaf Of A Sacred Tree To Reduce Medical Waste
The researchers used leaves from a Bodhi tree (Ficus religiosa). The veins of the leaves have a fractal pattern that makes the surface highly flexible and shearable. Silver nanowires were attached to the leaf skeleton, and the surface was encapsulated in a biodegradable transparent tape. (Click on title for full story.)
