Author: zooplantman
-
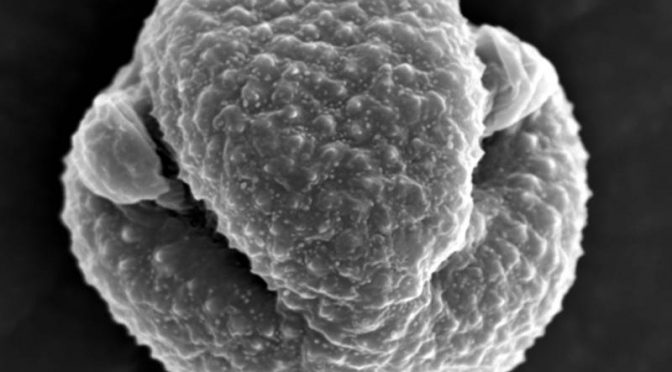
Asthma Sufferers: Bacteria That Can Trigger Attacks Hitchhikes On Plant Pollen
In the future, we will be able to indirectly use the pollen count to forecast very high levels of airborne endotoxin pollution. This will provide a useful warning for allergy and asthma sufferers,” (Click on title for full story.)
-

Milking It: Bugs Manipulate Plants’ Metabolism For Their Own Benefit
Free-living, sap-sucking bugs can manipulate the metabolism of their host plants to create stable, nutritious feeding sites.The discovery, published in eLife, shows that the bugs achieve this by copying plant hormones and injecting them into the leaves. They use a similar feeding strategy to endophytic insect species, which live inside plants. These findings could aid in the development of effective pest management strategies. (Click on title for full story.)
-

End Of The Line: Unsuitable Soils Will Halt Trees’ March Northward Due To Climate Change
It’s long been thought that climate change is enabling treelines to march farther uphill and northward. But it turns out that climate warming-induced advances may be halted by unsuitable soils. It is an important finding for resource managers looking to preserve individual species or entire ecosystems. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Recreating Mesozoic Environment To Learn About Vegetarian Dinosaur Nutrition
Scientists have measured the nutritional value of herbivore dinosaurs’ diet by growing their food in atmospheric conditions similar to those found roughly 150 million years ago. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Making Themselves At Home: Invasive Plants Adapt And Evolve Once Established
Scientists studied the characteristics of monkeyflowers (Mimulus guttatus), which first arrived in the UK from North America 200 years ago. They compared the behaviour of monkeyflowers long-established in Scotland with those introduced recently for the purposes of the experiment. Significantly, they found that the long-established plants were bigger and produced more flowers and more clones than those recently introduced. In comparison, the study showed that the genes of plants recently introduced are not well-adapted to deal with the UK environment. (Click on title for full story.)
-

More Farmland Will Result In More Climate Change?
If forests are cut down in favor of arable land and pasture land, it reduces the capacity of plants and soil to take up CO2. “The wood in a forest can store more CO2 than corn for example,” explains Arneth who in her research deals with the interaction between the atmosphere, plants and soil. If deforestation were to continue, it could even be expected that large parts of the tropics will change from a CO2 basin – which absorbs more CO2 than it releases – to a CO2 source. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Crowdfunded Study Discovers Origin Of Ferns’ Insecticidal Protection
The team found that the insecticidal gene is specific to the fern lineage, explaining why most other plants lack such resistance. Furthermore, they discovered that the gene likely first appeared in a fern genome through horizontal gene transfer from a bacterium. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Could This Common Garden Flower Be The Answer To Type-2 Diabetes?
Ten years ago, in an effort to produce a diabetes drug that specifically inhibits HPA activity without having nasty side effects, scientists screened 30,000 extracts derived from plants and other organisms and found a single compound that fit the bill: montbretin A (MbA) from the bulb-like underground corms of the ornamental plant montbretia (Crocosmia x crocosmiiflora). Unfortunately, MbA can’t be produced in large quantities without understanding the biochemical pathway and genes involved in its biosynthesis, a difficult task considering the diversity and complexity of plant metabolic pathways. (Click on title for full story.)
-

The Most Massive Living Organism, A Forest Of Clones, May Be Dying
The Pando spans 106 acres on a rolling hillside where it has overlooked the picturesque Fish Lake for thousands of years, possibly tens of thousands. But down among the trees it’s evident this iconic stretch of aspen trees, the most massive known organism on the planet, is in peril. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Save The Rain Forest? Record Years For Tropical Forest Loss
But such positive stories tend to be a relative rarity and experts say much more is needed to slow the pace of deforestation. To date, just 2 percent of international financing for activities to fight climate change goes toward forest conservation, said Frances Seymour, a senior fellow at the World Resources Institute. “We’re trying to put out a house fire with a teaspoon,” she said. (Click on title for full story.)
