Category: Plants & Medicine
-

At Long Last, Vital Plant Based Cancer Cure May Be Synthesized To Be More Easily Available
Plant scientists have taken the crucial last steps in a 60-year quest to unravel the complex chemistry of Madagascar periwinkle in a breakthrough that opens up the potential for rapid synthesis of cancer-fighting chemicals. (Click on title for full story.)
-

Herbal Does Not Equal Harmless: One Traditional Remedy’s Dangers Revealed
The authors of the study, therefore, call for increased vigilance regarding possible toxic effects of Evodia preparations. “The popularization of medicinal plants from other cultures entails risks. These plants can contain highly active substances with side effects, as in the case of Evodia. A closer examination of such risks is therefore indispensable to protect the…
-
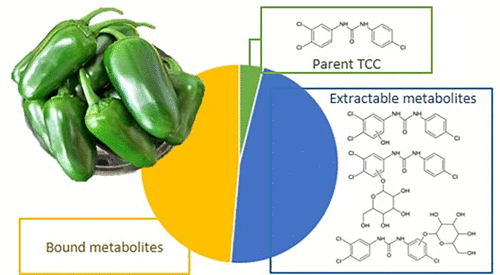
Antibiotics That Get Into The Water Supply Could End Up In Our Food
To track the antibiotic’s journey from water to pepper, the researchers labeled TCC with radioactive carbon (C14). They grew the pepper plants hydroponically and, after 12 weeks, sampled the C14 content in the roots, stems, leaves and fruit. While the pepper fruit itself had relatively low levels of TCC, it contained a hefty portion of…
-

Toxic Squash Syndrome: Who Knew?
Although it’s rare, other cases of cucurbit poisoning have been described in the medical literature; in those cases, people developed food poisoning after eating bitter-tasting squash, zucchini and other gourds, according to the new report. But these are the first two reported cases linking the consumption of bitter-tasting gourds with hair loss (Click on title…
-

You Want To Take Herbal Cures, But Can You Be Sure The Herb Is What It Says It Is?
“Thanks to globalization, special medicinal plants that grow in a single region only have a worldwide market,” says Peter Nick of KIT’s Botanical Institute. If the rapidly changing superfood trends lead to a sudden increase in demand, these often cannot be met by existing capacities, the professor for molecular cell biology says. The result is…
-
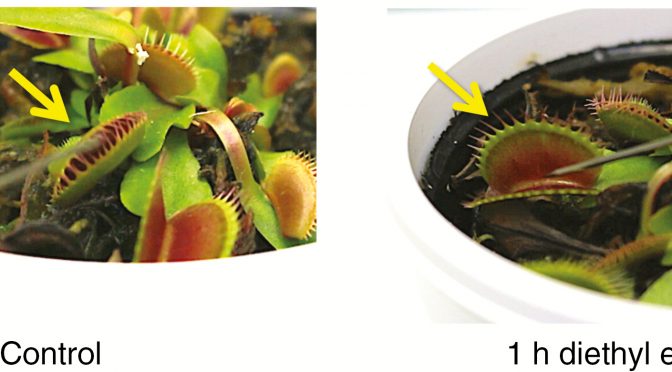
Human Anesthetics Work On Plants. Good For Research (Not Suggested Just For Pruning)
Plants are sensitive to several anaesthetics that have no structural similarities. As in animals and humans, anaesthetics used at appropriate concentrations block action potentials and immobilize organs via effects on action potentials, endocytic vesicle recycling and ROS homeostasis. Plants emerge as ideal model objects to study general questions related to anaesthesia, as well as to…
-

Asthma Rates In Urban Areas Reduced By Adequate And Appropriate Greenspace
We wanted to clarify how urban vegetation may be related to respiratory health. We know that trees remove the air pollutants which can bring on asthma attacks, but in some situations they can also cause localised build-ups of particulates by preventing their dispersion by wind. And vegetation can also produce allergenic pollen which exacerbates asthma. …
-

Is This Plant The Cure For The U.S. Opioid Crisis?
“There’s a huge wealth of anecdotal evidence, and some scientific, that there is definite medical potential for this plant. If it’s not in the treatment of mild and moderate pain, it’s definitely in the treatment of potential opioid withdrawal,” (Click on title for full story.)
-

The Amazing Moringa Tree: Medicine, Food, Fertilizer. What Can’t It Do?
If plants could be superheroes, the Moringa (Moringa oleifera) tree would be one of them. Although native to the foothills of the Himalayas in India, moringa can thrive in most tropical and subtropical regions. It is drought tolerant, grows rapidly, has leaves that can be used as a biofertiliser, and has seeds that can help purify water.…
-

Traditional Medicinal Plant Yields Cancer Shrinking Substance
Laboratory experiments show that the substance damsin in the plant Ambrosia arborescens inhibits the growth and spread of cancer stem cells. The similar substance, chemically produced by chemistry, has the same positive effect,. The plant Ambrosia arborescens grow wild in much of South America and is traditionally used as a medicinal plant. (Click on title for full story.)
