Category: Plants & Medicine
-
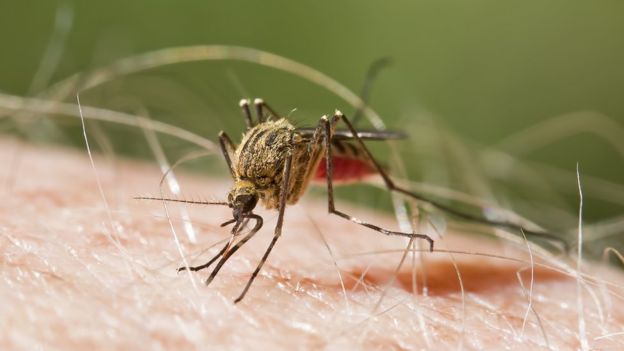
Controlling Malaria By Pruning Flowers Off Of Trees
Gardening could be a powerful weapon against malaria, culling mosquito populations by cutting off their food supply, say researchers.A team tested their idea in nine villages in the arid Bandiagara district of Mali, West Africa.Removing flowers from a common shrub appeared to kill off lots of the older, adult, female, biting insects that transmit malaria.…
-

Menopause Symptoms Eased With Fermented Red Clover
The vast majority of women in the menopause are familiar with the status of Red Clover as an herbal medicine that soothes hot flush symptoms and hormonal fluctuations. This holds true, new research shows, if the red clover is taken in a fermented form. Fermented Red Clover extract is demonstrated to decrease significantly both the…
-

Traditional Chinese Medical Herb Yields Promising Drug For Osteoporosis
The researchers tested a compound derived from red sage in human and mouse bone cells and a mouse model. They found that it prevented bone loss and increased the bone mineral density of the mice treated with the compound by 35 per cent, when compared with the control group. (Click on title for full story.)
-

New Drug Promise: Common Desert Shrub Produces Powerful Anti-Parasite Chemicals
Compounds produced by the creosote bush, a desert plant common to the Southwestern United States, exhibit potent anti-parasitic activity against the protozoa responsible for giardia infections and an amoeba that causes an often-lethal form of encephalitis. (Click on title for full story.)
-

New Technologies Could Turn Ancient Herbal Remedies Into Effective Drugs
We highlight several plant natural products that are either in the clinic or currently under active research and clinical development, with particular emphasis on their mechanisms of action. Recent efforts in developing modern multi-herb prescriptions through rigorous molecular-level investigations and standardized clinical trials are also discussed. Emerging technologies, such as genomics and synthetic biology, are…
-
Walnuts May Promote Micro-biota Health
“We found that walnuts in the diet increased the diversity of bacteria in the gut, and other non-related studies have associated less bacterial diversity with obesity and other diseases like inflammatory bowel disease,” (Click on title for full story.)
-
Researching The Untapped Health Benefits Of Edible Flowers
The growing need for nutraceutical new foods has generated interest in edible flowers.This flower trait inspired us to conduct experiments aimed at evaluating both the antioxidant activity and anthocyanin content in twelve species commonly used as ornamental plants. The antioxidant power of the edible flowers was very high compared to common vegetables and/or fruits. (Click…
-
Following Chimpanzees To Uncover Their Pharmaceutical Plant Secrets
These West African plants are part of a ‘jungle pharmacy’ sought out by wild chimpanzees to treat ailments ranging from worm infestations to bacterial infections. And because humans share 98% of their DNA with chimps, and are susceptible to some of the same diseases, they might work on people too. At least that is the…
-
Armenia’s Almost Lost Folk Medicine Reborn
Amasiatsi’s incredibly rich text advises on the uses of native Armenian plants in such depth that his writings continue to influence modern pharmacists, like Armen Sahakyan, a pharmacologist and botanical scholar who has been working at the Matenadaran Museum for the last several decades. A trained medical doctor ordained a deacon in 1997, Sahakyan has…
-
Does Use Of Anti-Fungal Drugs On Plants Endanger Human Health?
“Given that these fungi can persist for a long time, we are advising people not to plant tulip or narcissus bulbs in or near healthcare facilities or in the gardens of living quarters of patients who are in any way immunocompromised.” (Click on title for full story.)
